Expense accounts play a crucial role in tracking and recording various costs incurred by businesses. They help in determining the financial health of a company and assist in making informed decisions. In the realm of bookkeeping, credit entries are an essential aspect that affects expense accounts. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of credit to expense account entries, their impact on expense accounts, and the proper bookkeeping practices associated with them.
Credit to Expense Account
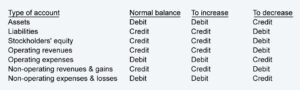
A credit entry is a financial transaction recorded in a company’s books that increases the balance of a specific account. In this case, a credit to the expense account indicates an increase in expenses incurred by the business. It is important to note that credit entries are made on the right side of a general ledger account.
Effect of a Credit Entry on an Expense Account
A credit entry to an expense account will increase it. This means that the total amount of expenses recorded in the account is higher. As a result, the net income of the business decreases, reflecting the impact of the additional expenses.
Instances when a Credit Entry is Made to an Expense Account:
- Recording daily operational expenses, such as rent, utilities, and office supplies.
- Accounting for specific project-related expenses, like travel costs or equipment rentals.
- Allocating indirect expenses, such as administrative overhead or marketing expenses.
Real Estate Expense Credit Card and Accounting
A real estate expense credit card is a specialized payment method designed for real estate professionals and property managers. It allows them to conveniently make purchases related to property management, maintenance, and repairs. Using such credit cards streamlines expense tracking and simplifies the accounting process.
Recording Real Estate Expenses in the Accounting System:
- Obtain detailed credit card statements: Regularly collect credit card statements to capture all real estate-related expenses.
- Identify and categorize expenses: Review each transaction on the credit card statement and categorize them based on the nature of the expense, such as maintenance, repairs, or property taxes.
- Create journal entries: Record the expenses in the appropriate expense accounts by making credit entries.
- Reconcile the credit card statement: Compare the recorded expenses with the credit card statement to ensure accuracy and resolve any discrepancies.
Proper Account for Crediting Real Estate Expenses:
When crediting real estate expenses, it is essential to use the appropriate expense account. Common expense accounts for real estate-related costs include:
- Repairs and Maintenance: This account is used to record expenses related to repairing and maintaining properties.
- Property Taxes: Expenses incurred for property taxes are credited to this account.
- Utilities: Any utility expenses, such as electricity, water, or gas bills, should be credited to this account.
Bookkeeping for Crediting Expense Accounts
Bookkeeping involves recording and organizing financial transactions in a systematic manner. It ensures accurate financial reporting and enables better decision-making.
When to Credit an Expense Account:
Expense accounts are credited when there is an increase in expenses. The following transactions require a credit entry to the respective expense accounts:
- Paying bills or invoices for goods and services.
- Making cash purchases of items directly related to business operations.
- Allocating overhead expenses to different departments or cost centers.
Examples of Transactions Requiring a Credit Entry to an Expense Account:
- Paying the monthly rent for office space would involve crediting the “Rent Expense” account.
- Purchasing office supplies using cash would require crediting the “Office Supplies Expense” account.
- Allocating a portion of the advertising expenses to the Marketing Department would involve crediting the “Advertising Expense” account.
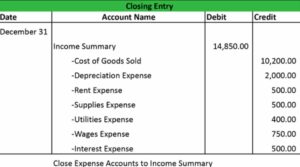
Closing Expense Accounts
Closing entries are made at the end of an accounting period to reset temporary accounts, such as revenue and expense accounts, to zero. The goal is to prepare the books for the next accounting period.
To close an expense account, a debit entry is typically made. This reduces the balance of the expense account to zero, preparing it for the next accounting period. The offsetting entry is a credit entry to the retained earnings account.
Determining Whether to Credit or Debit an Expense Account during Closing:
During the closing process, expense accounts are debited to reset their balances. However, if an expense account has an outstanding credit balance, it implies that the company received more credits than debits in that account during the accounting period. In such cases, a credit entry is made to close the account.
Increasing an Expense Account with a Credit Entry
Contrary to common perception, a credit entry to an expense account increases its balance. It signifies additional expenses incurred by the business during a specific period.
Impact of a Credit Entry on an Expense Account Balance:
When a credit entry is made to an expense account, it augments the total expenses recorded in the account, leading to an increased balance. This higher balance reflects the additional costs incurred by the business.
Examples of Transactions Resulting in Increased Expense Accounts through Credit Entries:
- Paying a vendor for professional services would involve a credit entry to the corresponding expense account.
- Charging employee salaries to the “Salaries Expense” account requires a credit entry to record the expenses.
Conclusion – Credit to Expense Account
Understanding credit entries in expense accounts is vital for accurate bookkeeping and financial reporting. By comprehending the impact of credit entries on expense accounts, businesses can maintain reliable financial records and make informed decisions. Properly credit to expense account and following sound bookkeeping practices contribute to the overall financial health and success of a company.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is a credit entry made to an expense account?
A credit entry is made to an expense account to reflect an increase in expenses incurred by the business. It is recorded on the right side of the general ledger account and contributes to the overall accuracy of the financial records. By crediting an expense account, businesses can track and monitor their expenditures effectively.
Q2. How does a credit entry affect an expense account balance?
A credit entry to an expense account increases its balance. This means that the total amount of expenses recorded in the account is higher. As a result, the net income of the business decreases, reflecting the impact of the additional expenses. Monitoring the balance of expense accounts helps businesses analyze their spending patterns and make informed financial decisions.
Q3. When should I credit an expense account?
Expense accounts should be credited in various situations, including:
- Paying bills or invoices for goods and services.
- Making cash purchases directly related to business operations.
- Allocating overhead expenses to different departments or cost centers.
Crediting the expense accounts accurately ensures that all expenses are properly recorded and accounted for, leading to accurate financial reporting.
Q4. How do I close an expense account at the end of an accounting period?
To close an expense account at the end of an accounting period, you typically make a debit entry to reduce the account’s balance to zero. The offsetting entry is a credit entry to the retained earnings account. This process ensures that temporary accounts, such as revenue and expense accounts, are reset for the next accounting period and helps maintain the integrity of financial statements. It is essential to follow proper closing procedures to ensure accurate financial reporting and analysis.